Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | We are wired for story. We crave it. Storytelling has played an integral role in our ability to make progress as a species. It should come as no surprise, then, that presenting data and information in story form maximizes the effectiveness of our communication. We can create deeper emotional responses in our audience when we present data in story form.
Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | Join data visualization expert Bill Shander as he guides you through the process of turning “facts and figures” into “story” to engage and fulfill our human expectation for information. This course is intended for anyone who works with data and has to communicate it to others, whether a researcher, a data analyst, a consultant, a marketer, or a journalist. Bill shows you how to think about, and craft, stories from data by examining many compelling stories in detail.
Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | Data visualization and analysis is the process of using visual elements like charts, graphs, and maps to explore, understand, and communicate patterns and insights found within data. It is a critical skill for making data-driven decisions across all industries, from business to science.
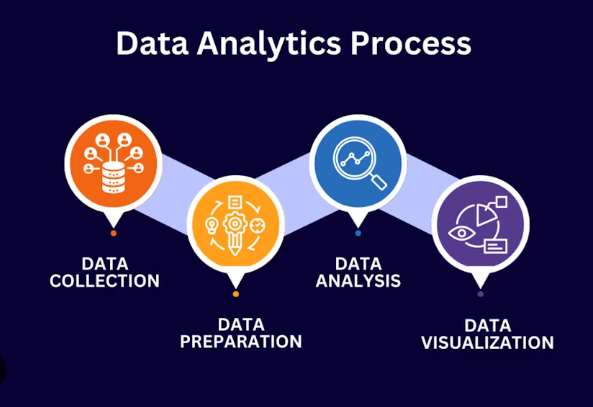
The data analysis process
Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | The data analysis process is a structured approach that transforms raw data into actionable insights. While the exact number of steps can vary, a common framework includes the following phases:
- Define the objective: Clearly state the business problem or research question you intend to answer. This provides focus and ensures the analysis delivers relevant and valuable insights.
- Collect the data: Gather the necessary data from internal or external sources, such as databases, surveys, or public datasets.
- Clean and process the data: Prepare the raw data for analysis by removing errors, duplicates, and irrelevant information. This step also involves handling missing values and structuring the data for easier manipulation.
- Analyze the data: Explore the cleaned data to identify trends, patterns, and relationships. Common analysis types include:
- Descriptive analysis: Summarizes and describes the main features of the data (e.g., calculating mean, median, and mode).
- Diagnostic analysis: Investigates the root cause of past events or outcomes.
- Predictive analysis: Uses historical data to forecast future trends.
- Prescriptive analysis: Recommends actions to take based on the predictions.
- Visualize and interpret the results: Present the findings using data visualizations and translate them into meaningful, actionable insights for stakeholders.
Common data Visualization techniques
Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | Different types of data and analytical goals require specific visualization techniques for effective communication.
- For comparing values:
- Bar/Column Charts: Excellent for comparing quantities across different categories.
- Bubble Charts: Can be used for comparisons by adding a third dimension represented by the size of the bubble.
- For showing trends over time:
- Line Charts: Ideal for displaying trends and changes in data over a continuous period, like months or years.
- Area Charts: Similar to line charts but with the area below the line filled, useful for showing cumulative data.
- For illustrating parts-of-a-whole:
- Pie Charts: Show the proportion of a whole, but are most effective with a limited number of categories.
- Tree Maps: Use nested rectangles to display hierarchical data as a part-to-whole relationship.
- For spotting correlations and distributions:
- Scatter Plots: Plot individual data points to show the relationship between two variables and identify correlations or outliers.
- Histograms: Display the frequency distribution of numerical data by grouping it into bins.
- For visualizing geographical data:
- Heat Maps: Use color gradients to represent data density or intensity on a map or another 2D space.
- Choropleth Maps: Shade geographic regions with colors that correspond to different data values.
Best practices for effective visualization

To ensure your visualizations are clear, accurate, and impactful, follow these guidelines:
- Know your audience: Adapt the complexity and detail of your visualization to their level of expertise.
- Choose the right visual: Select a chart type that is appropriate for your data and analytical purpose. For example, use a line chart for trends over time, not a pie chart.
- Keep it simple: Avoid clutter by eliminating unnecessary elements. Simplicity ensures your audience can grasp the key message quickly.
- Use color wisely: Apply color strategically to highlight important points and maintain consistency. Avoid using too many colors, which can be distracting.
- Provide context: Give your visualization a clear and informative title, labels, and annotations to guide the audience’s interpretation.
Popular tools for data Visualization and analysis
Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | Of course. Here is a comprehensive and structured outline for a Data Analysis and Visualization Course.
This curriculum is designed to take a student from foundational concepts to advanced techniques, using the most popular and powerful modern tools.
Course Title: Data Analysis and Visualization: From Data to Insights
Target Audience: Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | Aspiring data analysts, business analysts, marketers, researchers, project managers, and anyone who needs to make data-driven decisions.
Prerequisites:
- Basic computer literacy.
- Familiarity with working with data in any form (e.g., Excel spreadsheets) is helpful but not mandatory.
- No prior coding experience is required (the course will introduce it).
Course Goal: To equip students with the end-to-end skills to collect, clean, analyze, and visualize data to find insights, tell compelling stories, and support business decisions.
Detailed Course Modules
Module 1: Foundations of Data Analysis

- 1.1 Introduction to the Data Analysis Workflow: Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam |The non-linear process of asking questions, data acquisition, preparation, exploration, analysis, visualization, and storytelling.
- 1.2 Types of Data: Structured vs. Unstructured data. Understanding data types: Numerical (Discrete, Continuous), Categorical (Nominal, Ordinal), Dates.
- 1.3 The Tools of the Trade: Overview of the modern data stack: Spreadsheets (Excel/Sheets), SQL databases, BI tools (Tableau/Power BI), and programming languages (Python/R).
- 1.4 Introduction to Statistics for Analysis:
- Descriptive Statistics: Mean, median, mode, standard deviation, variance, quartiles.
- Basic Inferential Statistics: Understanding correlation vs. causation, confidence intervals, and hypothesis testing at a conceptual level.
Module 2: Data Acquisition and Wrangling (The “Data Prep” Phase)
- 2.1 Data Sourcing: Where to find data (internal databases, public datasets, APIs, web scraping concepts).
- 2.2 The Most Important Step: Data Cleaning: Identifying and handling missing data, duplicate data, and outliers. Standardizing formats.
- 2.3 Data Transformation: Creating new calculated fields, grouping data, pivoting and unpivoting data.
- 2.4 Hands-on Tools:
- Excel/Google Sheets: Power Query (Get & Transform) for intuitive data cleaning.
- Python (Pandas library): Introduction to DataFrames for programmatic data wrangling (covered in a later module).
Module 3: Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- 3.1 The Goal of EDA: Using visual and quantitative techniques to understand the patterns, relationships, and anomalies in your data before formal modeling.
- 3.2 Univariate Analysis: Analyzing single variables using summary statistics and visualizations like histograms, box plots, and bar charts.
- 3.3 Bivariate/Multivariate Analysis: Analyzing relationships between two or more variables using scatter plots, correlation matrices, and heatmaps.
- 3.4 Hands-on Tools: Performing EDA in Python with
pandas,numpy, andmatplotlib/seaborn.

Module 4: The Language of Data Analysis: SQL
- 4.1 Introduction to Relational Databases: What are databases, tables, rows, and columns?
- 4.2 Core SQL Queries:
SELECT,FROM,WHERE,ORDER BY,LIMIT. - 4.3 Aggregating Data:
GROUP BY,HAVING, and aggregate functions (COUNT,SUM,AVG,MIN,MAX). - 4.4 Combining Data: Using
JOIN(INNER, LEFT, RIGHT) to combine data from multiple tables. - 4.5 Practical Application: Writing queries to answer real business questions from a sample database (e.g., Northwind, Sakila).
Module 5: Programming for Analysis: Python Fundamentals
- 5.1 Why Python for Data Analysis? Introduction to the ecosystem.
- 5.2 Python Basics: Variables, data types, lists, dictionaries, and basic control flow (
ifstatements,forloops). - 5.3 Key Data Analysis Libraries:
- Pandas: DataFrames – the workhorse for data manipulation.
- NumPy: Numerical computing.
- Matplotlib: Foundational plotting library.
- Seaborn: High-level statistical visualization built on Matplotlib.
- 5.4 Hands-on Lab: Loading a dataset, performing basic cleaning, and creating simple plots.
Module 6: The Art and Science of Data Visualization
- 6.1 Principles of Effective Visualization: Understanding the goal of a viz: to enlighten, not decorate.
- 6.2 Choosing the Right Chart:
- Comparison: Bar charts, column charts.
- Relationship: Scatter plots, bubble charts.
- Composition: Pie charts (use sparingly!), stacked bar charts, treemaps.
- Distribution: Histograms, box plots, violin plots.
- Trends: Line charts.
- 6.3 Human Perception and Cognitive Load: How the brain processes visual information. Using pre-attentive attributes (color, size, position) effectively.
- 6.4 Dashboard Design Principles: Layout, storytelling, interactivity, and audience targeting.
Module 7: Business Intelligence (BI) and Dashboarding Tools
- 7.1 Introduction to Modern BI Tools: Tableau vs. Power BI vs. Looker (key differences and use cases).
- 7.2 Deep Dive into a BI Tool (e.g., Tableau Public):
- Connecting to various data sources.
- Building basic charts and calculated fields.
- Creating interactive filters and parameters.
- Designing and formatting a cohesive dashboard.
- 7.3 Publishing and Sharing Insights: How to share dashboards with stakeholders.
Module 8: Capstone Project – The Full Story
- 8.1 Project Definition: Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | Students choose a dataset and define a business problem or key questions to answer.
- 8.2 End-to-End Workflow: Students will:
- Acquire their data.
- Wrangle and clean it (using Python or a tool of their choice).
- Explore it (using SQL and/or Python).
- Analyze it to find key insights.
- Visualize it in a dashboard (using a BI tool like Tableau or Power BI).
- 8.3 Final Presentation: Students present their findings, telling a compelling data-driven story to “stakeholders” (the class and instructor).
Recommended Tools & Technologies
- Spreadsheets: Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets (with Power Query/Get & Transform)
- Database & SQL: PostgreSQL or MySQL (free, industry-standard)
- Programming: Python (using Jupyter Notebooks via Anaconda distribution)
- Visualization: Tableau Public (free) or Power BI Desktop (free)
- Version Control: Basic introduction to GitHub for storing code

Learning Outcomes
Upon completion, students will be able to:
- Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | Navigate the complete data analysis lifecycle from question to insight.
- Write basic to intermediate SQL queries to extract and aggregate data from databases.
- Use Python and the Pandas library to clean, manipulate, and explore datasets.
- Apply principles of effective visual communication to create clear and impactful charts.
- Design and build interactive dashboards in a leading BI tool (Tableau/Power BI).
- Synthesize analysis into a compelling narrative to inform and persuade stakeholders.
Analysis And Visualization Course in Visakhapatnam | This course balances practical skill-building with foundational theory, ensuring students not only know how to use the tools but also why they are making specific analytical and visual choices.